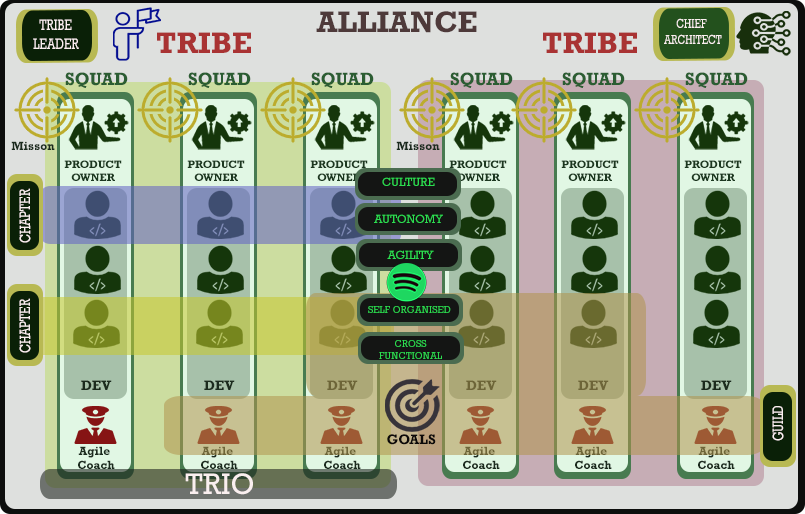
This lecture focuses on the music streaming service called Spotify. The organisation changed its culture to create a less rigid form of Agility that focuses on agile principles rather than Scrum practices. The lightweight framework is adopted by engineering disciplines and more focused empirical teams.
Spotify Framework
Spotify is a Swedish streaming service formed in 2008. It started as a Scrum organisation that thrived on the Scrum principles and values. Once the practices were matured and embedded into the organisation questions were being raised about the rigidity and the scaleability of Scrum practices and a highly-scaled light-weight framework was created called Spotify Agile.
The organisation took a more direct approach to adapt and focus more on the Agile principles and less on the Scrum practices. The transition away from Scrum meant that roles such as the Scrum Master would need to be changed, and this role evolved towards the Agile Coach. One of the key principles is to focus on Self-organised, Cross functional teams based on the Agile principles and drive autonomy within the teams. Henrik Kniberg and Anders Ivarsson were the first to introduce this model to audiences in 2012.
Spotify Principles
The Agile principles is a key pre-requisite for Spotify framework. Each of the principles are the pillars that drive the organisation and not the practices and its about its people and its culture.
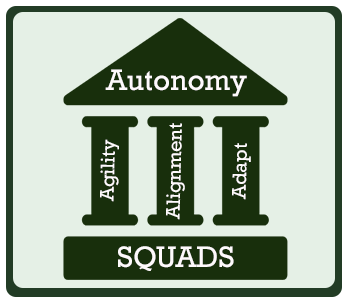
The main pillars for Spotify are Autonomy is often seen as the foundation for the framework. A key characteristic is that the Squad has direct access to the stakeholders.
Adapt easily
Adaptation is the action or process of changing something, a good example of this is Backlog grooming and adding stories or acceptance criteria's, Story estimation and prioritisation .
Ensuring that the three pillars feature prominently in the way Scrum is done is vital, it allows oneself to keep to the goals that drive the quality on the product being built and engages the whole team on what need to be done and how.
Spotify Values
The scrum team abide by the 5 core values or competencies, everyone within the Scrum focus on the clear objective - Sprint Goal. All team members work collaboratively using the values to deliver a increment of 'Done'. The transparency of the work by the team ensures that the values can be achieved.
Each scrum members use the pillars and the values to unite on the focus on what is to be achieved, and each agrees on the way to work, improve and address challenges that may confront them. This is the clear essence of Scrum.
Values help in the way the team interacts and the approach that is taken. Each shapes the thought processes around how things are done, and more importantly why we do them,
Squad Structure
Squads Team
The basic unit of development in Spotify is the Squad. The concept based on a Squad team is based on Agile principle No 5:
Agile Principle #5
"..Build projects around motivated individuals. Give them the environment and support they need, and trust them to get the job done.."
Spotify embrace this principle around our mindset of the Squads team. The Squad team consists of empirical members who are able to guide each other and have there own area of expertise. They are deemed as a mini start-up. They are leaders in their own right, and have an equal role and standing within the group. There is no hierarchy and no leader. The whole of the development team is accountable for the delivery .
In most Agile frameworks development teams are described as 'cross Functional', 'self organised' and 'empowered' teams.
It is vital that the Spotify team are kept to the maximum limit of 12, this is gauged as the optimum velocity a team can perform at it's most efficient.
Having small Squad teams emphasises focused delivery allowing highly skilled power teams deliver the product or features. There are 3 main roles in a Squad team: Agile Coach, Product Owner and the development/engineering team.
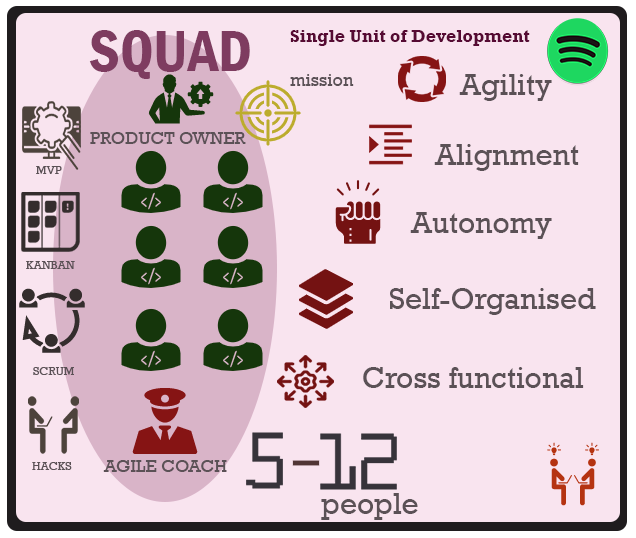
It is important to emphasize, there is No leader in the Squad team and each Squad has its own mission. The Agile Coach or Product Owner is in an equal par as the developer. They're skillsets fit like a glove embracing their collective knowledge and experience motivated towards the team success.
Hack Days
Squad teams are encouraged to engage in hacks or hackathons, these are events where team members engage in any innovative or learning techniques to drive motivation and encouragement in their teams as well as emerging technology. Teams can decide anything they want to do during these hacks. Hacks can take place once every fortnight upto a week hackathon.
Tribes
A Tribe by definition is a collection of Squads that can be grouped as themes. The main objective for these Tribes is to drive collaboration between Squads and ensure transparency between these teams are clear. Each Tribe has a leader (Tribe Leader) and teams are often located in the same building and hubs where the collaboration is likely.
Tribes are split into the themes that Squad teams work on, for example, some of the team may be working on a particular service area, another in infrastructure component and another in a delivery component.
A limit of upto 100 people can be assigned to a Tribe and groups are asigned to the principle of Dunbar number based on social groups and interaction.
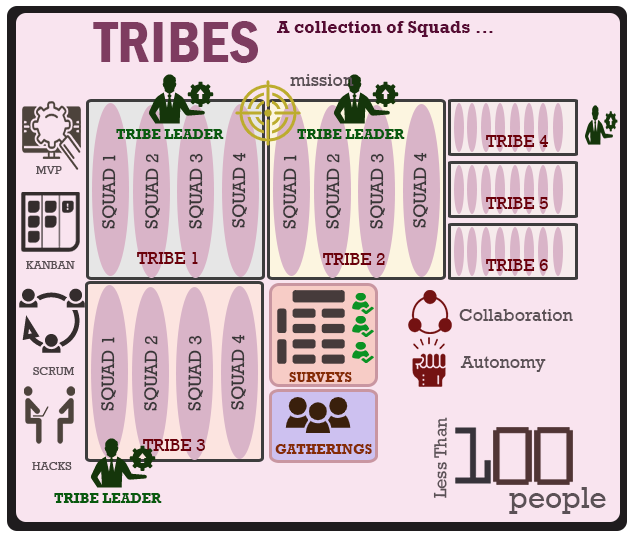
Gatherings
These are ceremonies that Tribe members perform on a regular basis and set in less formal environment. The main objective is to show transparency to the teams on retrospective learnings, demonstrations or hackathons.
Chapters and Guilds
A Chapter is formed by members of a Squads in a single Tribe having very similar skillsets or tooling and is regarded as the 'glue that keeps the organisation together'. Each Chapter will have a chapter lead and Chapter members.

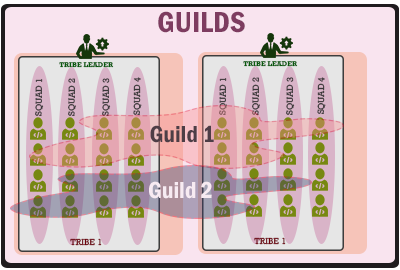
Guilds
This is a group of people across Tribes and Squads that participate in knowledge, tools and techniques to encourage development and problem solving across Squads and Tribes. Keeping teams aligned is a clear driver for Guilds and provides focus. Any member of a Squad, Tribe and Chapter can participate in a Guild.
Roles and Responsibilities
The three main roles inside scrum are:
1Agile Coach

The Agile Coach is the servant-leader where the main goal is to serve the Squad.
Each Squad has access to an Agile Coach where they serve the development team and also advocate the agile mindset and practices to both the business and the Squads. The focus is to coach the team or 1:1 coaching.
They align themselves to remove any impediments or blockers that may arise in the process and actively ensure the facilitation for squad activities or ceremonies in either Scrum or Kanban. They also ensure the retrospectives are actually learnt and improved over time.
Agile Coach is not a bottleneck to the Squads.
In Scrum Teams a scrum master heads up a lot of the ceremonies and communication between the stakeholders and development activities. This is often deemed as a non agile practice and the Agile Coach will participate but not directly affect how the development team does its tasks but improve the agility in completing those tasks.
The responsibility on how the work is completed falls on the roles of the full development team. The Agile Coach ensures there is no single point dependency on a person and the team can operate effectively with no impediments whatsoever.
2Product Owner

The product owner is the proxy business representative for the Squad team. They ensure that requirements that come from the business are shaped and understood for the development team to execute. The Product Owner is not involved or interested in how the work is completed by the Squads.
The Business Vision for the work needs to be understood by the Scrum team so it is imperitive that the Product Owner understands the product, and the needs of the business. The other main tasks for the product owner is to manage and prioritise the backlog
The product owner is the single owner of the backlog, every item needs to be authorised and approved by the PO before it will go into the backlog for prioritisation. Other duties for the Product Owner include
Maintain Roadmap
Maintaining the Roadmap in an highly scaled environment to ensure transparency with other Squads and Teams.
Backlog Grooming
Maintaining the backlog is one of the main tasks for the product owner. Ensuring user-stories are created are accurate and contain acceptance criterias and have clear business value and old user-stories are removed.
Story Mapping
Working with stakeholders to create user-stories are also vital. Having accurate stories enable the development teams to deliver exactly what the user wants. Story mapping is a technique that allows stories to be created at epic level.
Writing user-stories
User-stories are a subset of story mapping - the single unit of a feature to be developed. Generally stories created are based on the behavioural appraoch where customers behaviours are captured in terms of the requirements.
Story walkthrough
Once requirements are captured these will need to discussed with the development teams for delivery.
Prioritisation
Prioritising items from the backlog
Liaise with scrum master
The Product Owner and Agile Coach work closely together, particularly during the Sprints.
The Product Owner and Agile Coach work closely together, particularly during the Sprints.
3Development Team
The development team are responsible for the execution and delivery of the Sprint. It is here that the emerging detail is defined as increment of 'Done' will be created.
They will translate the user-story into functional and non-functional needs. The developers are empowered to make day to day decisions according to their area of expertise. All sub-tasks for the user-story are created, all dependencies are defined and all test documents are prepared during the Sprint.
The Development team consists of Developers and QA testers. I have also included the Business Analyst (although the role has not been stated in the scrum guide), this is because they are a key dependency during the Sprint to support the team.
Squad Artifacts
These are information radiators to visualise the work to be channelled to the development team in the shape of the Product Backlog, Sprint backlog, Product Increment and the Burn-down Chart.
Burndown Chart
During the sprint the total work remaining to reach the Sprint goal is calculated using the Burndown Chart. The Product Owner uses this chart to determine not only the effort remaining and whether the intended target will be met, but also determining the velocity of the sprint based on previous historical sprints.
The burndown is a good visual indicator of the work remaining during the sprint and the whether the team will achieve the intended target for the sprint goal. Any user-stories that have not been completed are termed as 'Spill overs'. The burndown chart is very god indicator as to whether the team is on track - but there is a strong emphasis on the scrum team logging the time recorded in order to keep the track up to date.